

Impaired language function ( dysphasia) during or soon following a seizure is more likely to occur when seizures arise from the language dominant side of the brain. In comparison to mesial temporal lobe seizures, lateral temporal lobe seizures are briefer duration seizures, occur with earlier loss of awareness, and are more likely become a focal to bilateral tonic-clonic seizure. Lateral temporal lobe seizures arising from the temporal- parietal lobe junction may cause complex visual hallucinations. The common auras from seizures arising from primary auditory cortex include vertigo, humming sound, ringing sound, buzzing sound, hearing a song, hearing voices or altered hearing sensation.
right arm dystonic posture arising from a left temporal lobe seizure. A dystonic posture on one side of the body commonly indicates seizure onset from the opposite side of the brain e.g.

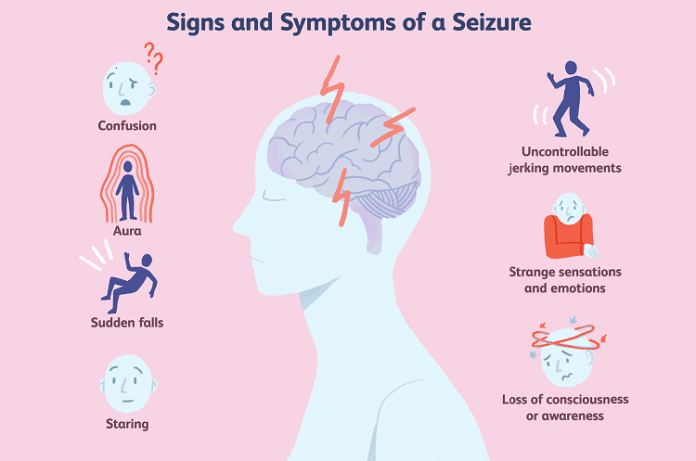
Dystonic posture is an unnatural stiffening of one arm occurring during a seizure. Repeated stereotyped motor behaviors ( automatisms) may occur such as repeated swallowing, lip smacking, picking, fumbling, patting or vocalizations. A person may then stare blankly, appear motionless ( behavioral arrest) and lose awareness. The common mesial temporal lobe seizure auras include a rising epigastric feeling, abdominal discomfort, taste (gustatory), smell (olfactory), tingling (somatosensory), fear, déjà vu, jamais vu, flushing, or rapid heart rate ( tachycardia). Symptoms and behavior Medial temporal lobe epilepsy ĭuring a temporal lobe seizure, a person may experience a seizure aura an aura is an autonomic, cognitive, emotional or sensory experience that commonly occurs during the beginning part of a seizure. A focal impaired awareness temporal lobe seizure occurs if a person becomes unaware during any part of the seizure. A focal aware temporal lobe seizure occurs if a person remains aware of what occurs during the entire seizure awareness may be retained even if impaired responsiveness occurs during the seizure. The ILAE 2017 classification distinguishes focal aware from focal impaired seizures. The less common lateral temporal lobe or neocortical temporal lobe seizures arise from the outer ( lateral) temporal lobe. Temporal lobe epilepsy is the most common focal onset epilepsy, and 80% of temporal lobe epilepsy is mesial (medial) temporal lobe epilepsy, temporal lobe epilepsy arising from the inner ( medial) part of the temporal lobe that may involve the hippocampus, parahippocampal gyrus or amygdala. Temporal lobe epilepsy occurs from seizures arising within the temporal lobe. Under the International League Against Epilepsy (ILAE) 2017 classification of the epilepsies, focal onset epilepsy occurs from seizures arising from a biological neural network within a single cerebral hemisphere.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
